Tools from 2 million years ago have been discovered. The Praluids left Africa earlier than thought
Human ancestors reached Asia at least 2.1 million years ago, scientists say. Stone tools and bones found in central China represent the earliest known traces of the existence of our ancient relatives outside Africa.
According to recent reports from scientistsów, human ancestors left Africa earlier than previously thought. Artifacts found in China suggest that our cousins colonized East Asia more than two million years ago.
A publication on the subject appeared in the journal „Nature”.
Most researchers argue that hominins – an evolutionary lineage spanning róalso human-they first left their African homeland about 1.85 million years ago, but Chinese finds challenge this concept. They force scientistsów to be reconsidered, które species first left Africa – and when it happened.
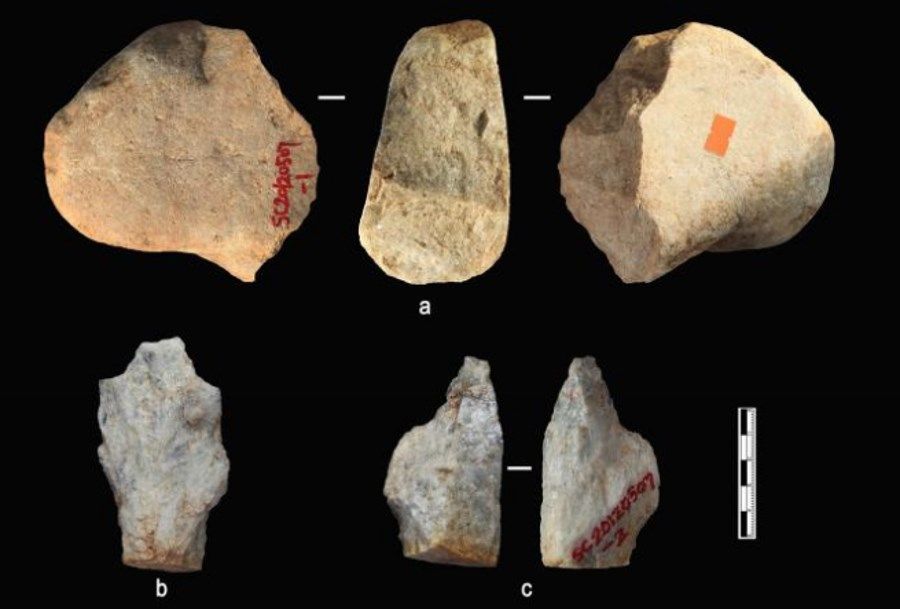
The tools were discovered in the village of Shangchen in central China. Loess layers, in whichórym they have been found are between 1.26 and 2.12 millionóat lat. So far, the oldest traces of the ancestral presence of theóin humans outside Africa were considered remains and tools found in Dmanisi, Georgia. The finds from China, however, are about 270,000 years older. years.
The tools are made of quartzite. They are relatively simple, but this is a typical feature of all stone tools from such early archaeological history. They all bear traces of use and scientists have no doubt that they were made on purpose. Material from whichórgo were made probably comes from gór Qin Ling, located about 5–10 kilometerów from the site where the tools were discovered. Bones of animals were also discovered at the site where the stone artifacts were found, któof which dating indicated a similar age to the soil layers – 2.12 million years old.
The discovery was made by a team ofół Chinese and British geologistsów and archaeologistów led by Zhaoyu Zhu of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Robin Dennell of the University of Exeter.
Researchers found a total of 96 stone objectsóin the Lesser Highlands. 80 of them were found in layers of soil, które suggest a warm and humid climate. 16 others lay buried in layers of loess, whichórego analysis indicates a cooler and drier climate.
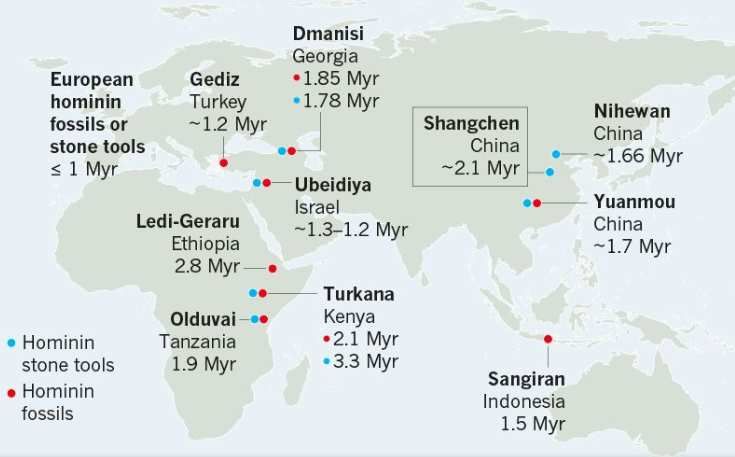
The oldest ancestral traces foundóin humans, fot. Nature (Myr – million years ago)
Researchers have dug through a total of 17 layers of settlementsóin loess covering a period of nearly one million years. In their opinion, our early ancestors inhabited this Chinese loess plateau in rótion of climatic conditions from 1.2 to 2.12 million years ago.
– Our discovery means that the moment should now be reconsidered, in which theóhe first humans left Africa – admitted Professor Dennel.
The identity of the twórców tools is currently unknown. No hominin bones were found near the site where the tools were discovered. However, researchers acknowledge that it is difficult to excavate in the area because of the well-developed agriculture, whichóre occupies a large part of the plateau. Therefore, the search for the remains ofóin pralids should be put down on póThe later period.
– We would all like to find a hominin – preferably with a tool in hand – joked Dennel. Researchers point out that one possibility is Homo erectus. It was the remains of this species that were found in Georgia. It is known that the representative Homo erectus left Africa 1.7 million years ago, so they are a natural candidate for twórcóIn stone tools found in China. Dennel believes, however, that the twórcy objectów belonged to an earlier species of the genus Homo.