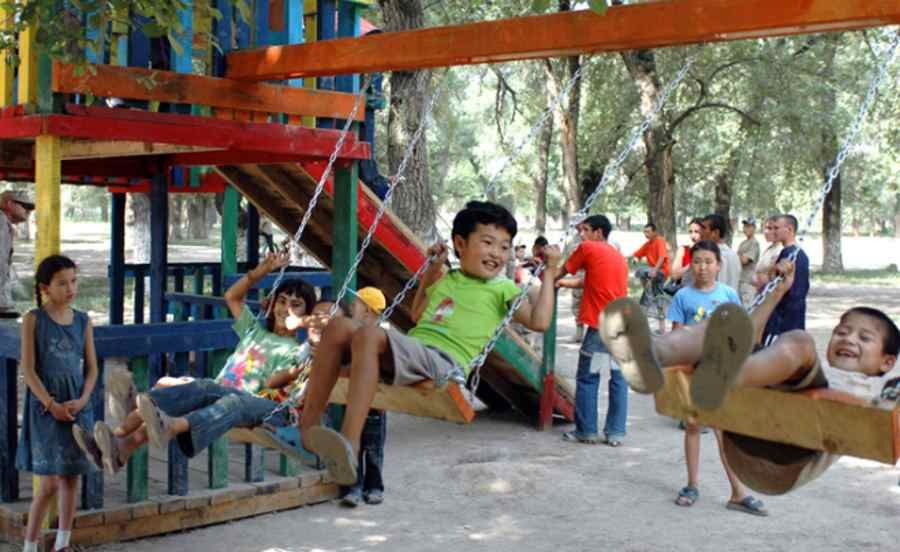
Why do children have so much energy? Scientists have found the answer
All adults who have fallen from fatigue while playing with children have asked themselves this question. Why do they have such indefatigable forces? Scientists have found the answer: children have higher energy levels than professional athletes.
In the survey, któHowever, so far we have not seen any results published in the journal „Frontiers in Physiology” poreówn were studied energy production and recovery rates after exercise in young boysóIn, non-training adults and professional athletesóin those training in endurance sports.
– Our research has shown that aerobic metabolism is used more efficiently in children. This is why they are less fatigued during intense exercise – said Sebastien Ratel of Universite Clermont Auvergne in France, whoóry led the research.
Previous studies have already shown that children do not fatigue as quickly as non-exercising adults during physical exercise. It was then suggested that they had an energy profile cfócomparable to endurance athletes, but until now there was no evidence of thisów.
The research was conducted on three groups. The first consisted of 12 young boysów ages 8 to 12. The second was 12 adult, but untrained men. The third group included professional athletes celebrating success in endurance sports such as triathlon, marathons and cycling.
All groups performed the same aerobic and anaerobic exercises. They were m.in. two seven-second sprints with a one-minute break, during which theóved measured aerobic and energy output, or a 30-second exercise test on a stationary bicycle. During exercise, heart rate, blood oxygen levels and the time taken to remove lactic acid from the blood were studied. In all tests, children performed better than untrained adults.
It has been found that children not only have muscles that are resistant to fatigue, but róThey also recover quickly from high-intensity exercise – even faster than athletes. The researchers calculated that during the testóin exercise power of adults dropped 51.8 percent, athletesów by 41.8 percent., But children only by 35.2 percent.
– Children recover very quickly. Faster than well-trained athletes, as evidenced by their faster stabilization of heart rate and ability to remove lactic acid from the blood. This may explain why the children seem to have unquenchable strength to play, long after the adults have lost it – admitted Ratel.
Researchers are confident that the findings can helpóc in the development of athletic potential in children, as well as a better understanding of how our bodies change during the transition from childhood to adulthood.
– Many parentsów asks about the best way toób on developingój their child’s sports potential. Our study shows that muscular endurance is often very good in children, so it is better to focus on other areas of fitness, such as sports technique or sprint speed. It may helpóc optimize physical training in children to play better and enjoy sports more – explained Anthony Blazevich of Edith Cowan University in Australia, coórouter of the study.
– As the chorób associated with physical inactivity, it is helpful to understand the physiological changes that accompany adolescence, whichóre may contribute to the risk of many diseasesób. Our research indicates that aerobic capacity, at least at the muscular level, decreases significantly with age, which may influence the increase in the incidence of diabetes, for example – noted Ratel.